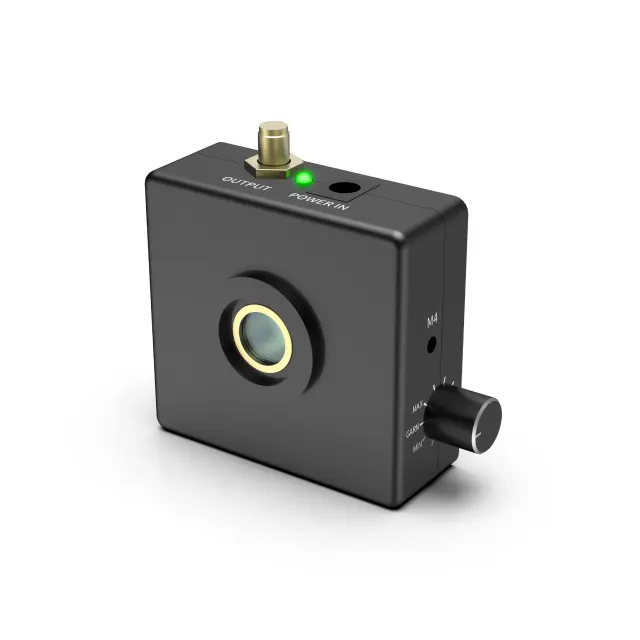



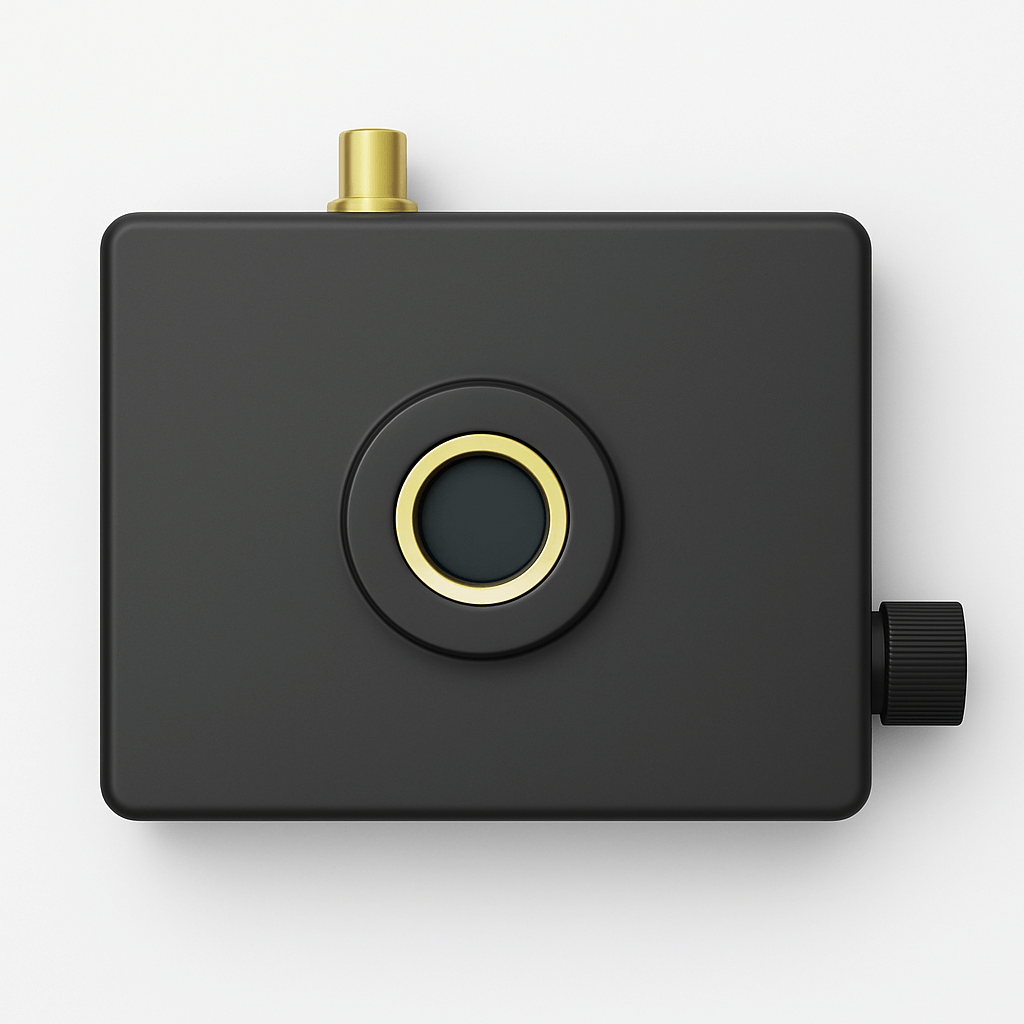
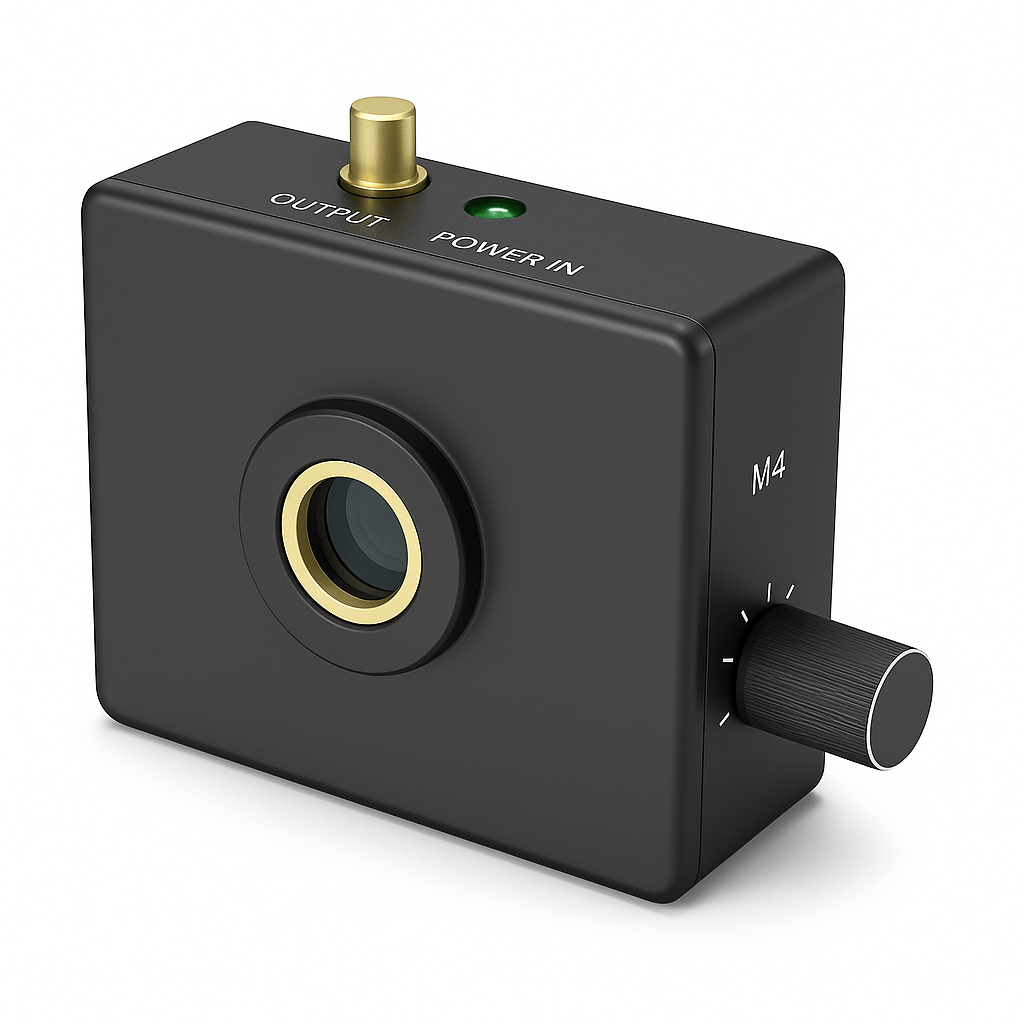
This product is a compact near-infrared avalanche photodetector with a core circuit made of domestically produced InGaAs/InP APD with independent intellectual property rights. It has characteristics such as high gain, high sensitivity, and low noise. It can provide a cost-effective solution for near-infrared weak light detection and measurement of short pulse signals, and is widely used in fields such as laser communication and LiDAR.
This product operates in linear mode and integrates a low-noise broadband transimpedance amplifier, achieving a maximum conversion gain of 5.2 x106V/W and supporting gain adjustment; Using temperature compensation circuit to achieve temperature stability control of signal amplification factor. The diameter of the photosensitive surface reaches 200 μm, At a working bandwidth of 10MHz, the noise equivalent power is as low as 0.35nW; Support free space coupling and fiber optic coupling; Meanwhile, the internally integrated strong light injection protection function enables the product to have higher environmental adaptability.
-High gain
-High sensitivity
-Low noise equivalent power
-Strong light injection protection function
-Optional light incidence mode

522KB
| TECHNICAL PARAMETER | TECHNICAL INDEX |
| Product model | QCD 200A |
| Wavelength range | 900nm~1700nm |
| Photosensitive surface diameter ª | 200μm |
| Maximum gain efficiency @(RL=500) | 5.2×10⁶ V/M |
| Maximum output voltage @(RL=500) | 2.1V |
| Output bandwidth ᵇ | DC~10MHz |
| Noise equivalent power(DC~1MHZ) | |
| Total noise power(DC~10MHZ) | 0.35nW |
| Optical coupling | Free space coupling /optical |
| Output DC bias | < ±25mW |
| Input voltage | 12V |
| Dimensions | 60mm×56.5mm×22mm |
| a : Photosensitive surface size can be customized b : Output bandwidth can be customized | |
-LiDAR
-Laser ranging
-Laser communication
-Time city reflection of light

Visible Light⁺ Near-Infrared Camera
This camera is suitable for the spectral range of 400-1700nm, covering the visible light to shortwave

InGaAs Linear Focal Plane Camera
The industrial grade linear array shortwave infrared camera is designed for the spectral ange of 900-1700nm

InGaAs Face Array Focal Plane Camera
This product uses domestically produced high sensitivity InGaAs array detectors, with array sizes of 320×256

InGaAs Avalanche Photon Detector
This product is a compact near-infrared avalanche photodetector with a core circuit made of domestically

Time-to-Digital Converter
The QTDC-16CH-0A is a compact, high-precision measurement instrument featuring 16 acquisition

Single Photon Ranging System
This product adopts a fiber optic coaxial optical path design and an integrated system design,which has good stability
InGaAs (Indium Gallium Arsenide) Avalanche Photodetectors (APDs) represent a critical advancement in photonic detection technology, particularly for near-infrared and short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) applications. These highly sensitive devices combine the inherent infrared sensitivity of InGaAs material with the internal gain mechanism of avalanche photodiodes, resulting in detectors capable of sensing extremely low light levels with high speed and efficiency.

Avalanche photodiodes operate on fundamentally different principles than standard photodiodes, providing internal amplification of the photocurrent. Unlike conventional photodiodes, APDs apply a high reverse bias voltage that approaches the breakdown voltage, creating strong electric fields within the semiconductor structure.
When photons are absorbed in an APD, they generate electron-hole pairs which are accelerated by the strong electric field. These accelerated carriers gain sufficient kinetic energy to create additional electron-hole pairs through impact ionization, initiating an avalanche multiplication process that amplifies the original photocurrent. This internal multiplication provides the high sensitivity that makes APDs valuable for detecting faint optical signals.
The avalanche photodiode concept was invented by Japanese engineer Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1952, though research on avalanche breakdown phenomena predated this patent. Since then, significant advancements have been made in both materials and device architectures.
InGaAs has become the material of choice for infrared detection in the 950-1700 nm wavelength range due to its exceptional optical and electrical properties. Unlike silicon APDs, which have limited sensitivity beyond 1100 nm, InGaAs-based detectors can efficiently detect light in the important telecommunications wavelengths around 1300 nm and 1550 nm, making them crucial components in modern fiber-optic systems
Most advanced InGaAs APDs employ a Separate Absorption, Grading, Charge, and Multiplication (SAGCM) structure, which optimizes device performance by dividing functionality across specialized layers:
Absorption Layer: Made of InGaAs, this layer absorbs incident photons and generates the initial electron-hole pairs. The layer thickness and doping profile are carefully designed to maximize photon absorption while facilitating efficient carrier extraction.
Grading Layer: This transitional layer between the absorption and charge regions prevents carrier accumulation and reduces recombination. As noted in research, “The addition of grading layer between the charge layer and the absorption layer can avoid the accumulation of holes in the charge layer, reduce the number of minority carriers’ recombination in the charge layer, and maintain the control effect of the charge layer on the device’s electric field”.
Charge Layer: This precisely doped layer controls the electric field distribution throughout the device, ensuring the field is sufficiently low in the absorption region to prevent premature breakdown while maintaining a high field in the multiplication region.
Multiplication Layer: Typically made of materials like InP or InAlAs, this high-field region is where avalanche multiplication occurs. The thickness and composition of this layer significantly influence gain, noise, and bandwidth characteristics.
Recent innovations in some devices have introduced multi-gain-stage structures that significantly enhance performance. These designs incorporate multiple avalanche regions in series, separated by carrier relaxation layers where the electric field is intentionally kept low. This architecture prevents avalanche feedback between stages, resulting in much higher stable gain and lower excess noise.
InGaAs APDs typically offer controllable gain factors from 1 to more than 100, with specialized designs capable of gains exceeding 6,000. This internal amplification significantly improves signal-to-noise ratio in photon-starved applications.
The frequency response of InGaAs APDs varies widely depending on design, with commercial products available in ranges from:
A key limitation of APDs is noise, which becomes more pronounced at higher gain values. This noise predominantly comes from:
InGaAs APDs have become essential components in numerous applications requiring sensitive infrared detection:
In fiber-optic telecommunications systems, InGaAs APDs serve as receivers that detect weak optical signals after transmission through long fiber spans. Their high sensitivity and good response speed make them ideal for high-bit-rate communication systems operating at 1300 nm and 1550 nm wavelengths.
The superior sensitivity of InGaAs APDs at eye-safe wavelengths (around 1550 nm) makes them particularly valuable for LiDAR applications in autonomous navigation, environmental sensing, and industrial measurement.
As reported in research: “The maximum detection range can be even further extended by the usage of laser sources for the short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) spectral range with typical wavelengths around 1550 nm, allowing for increased optical intensities to be emitted”.
In spectroscopic analysis instruments, APDs (Avalanche Photodiodes) are used to detect light signals at specific wavelengths, enhancing the precision and sensitivity of analyses.
In astronomical telescopes and spectrometers, APDs are employed to detect faint light signals from the cosmos, aiding scientists in studying astrophysical phenomena.
In the biomedical field, APDs can be integrated into imaging technologies such as fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) to deliver high-resolution images of cellular or tissue structures.
InGaAs APDs with gains up to 100 have set “a new standard for detecting low light intensity fluctuations, essential for advanced Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) systems”, used for characterizing and troubleshooting fiber optic networks.
An InGaAs Avalanche Photodetector is a light-sensing device that utilizes an InGaAs-based Avalanche Photodiode (APD) to detect and amplify weak optical signals in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range (typically 900–1700 nm).
InGaAs APD refers to the core photodiode component, which amplifies optical signals using avalanche multiplication.
InGaAs Avalanche Photodetector usually refers to a complete module that includes the APD along with supporting electronics like bias circuits, temperature controllers, and amplifiers.
Fiber optic communication
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
Quantum communication
Spectroscopy
Laser range finding
Medical imaging and diagnostics
The typical operating wavelength range is 900–1700 nm, with optimal performance at communication wavelengths like 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
Avalanche gain refers to the internal amplification of the signal caused by the avalanche multiplication process. It allows the detection of very weak optical signals, making the detector highly sensitive.
Dark current: The leakage current when no light is present.
Noise: Arises from shot noise and thermal noise.
Responsivity: The efficiency of converting light into electrical signals.
Breakdown voltage: The voltage at which avalanche multiplication begins.
InGaAs APDs have relatively low dark current and noise, but their noise increases with avalanche gain. Proper design of the biasing circuit and cooling can mitigate this.
High-performance modules often include thermoelectric coolers (TECs) to stabilize the temperature of the APD, as temperature fluctuations can affect gain and noise.